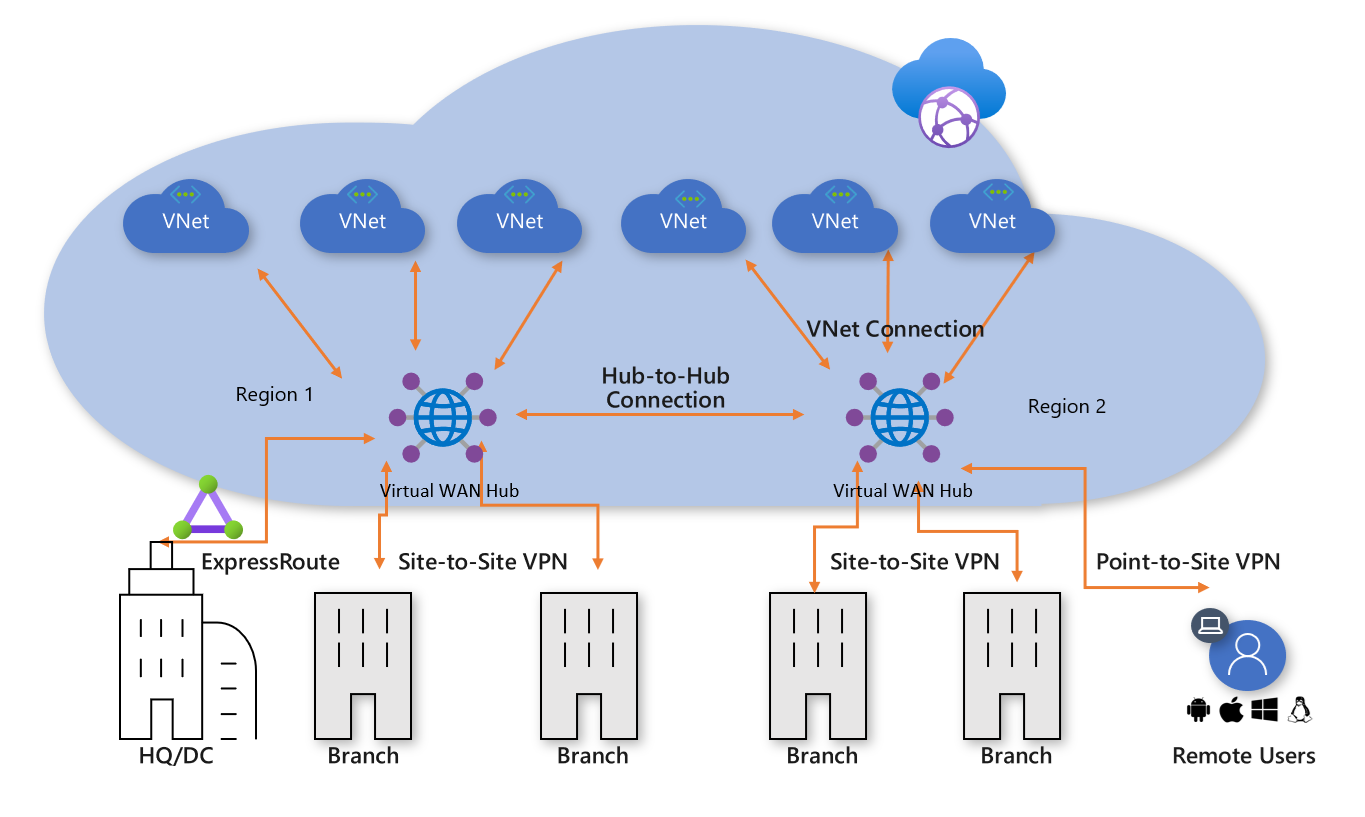
Azure Virtual WAN
Azure Virtual WAN is a networking service that brings many networking, security, and routing functionalities together to provide a single operational interface. Some of the main features include:
- Branch connectivity (via connectivity automation from Virtual WAN Partner Network Virtual Appliance devices such as vmWare SD-WAN or other VPN Customer Premises Equipment (CPE)).
- Site-to-Site VPN connectivity.
- Point-to-Site VPN connectivity.
- Private connectivity (Azure ExpressRoute).
- Intra-cloud connectivity (transitive connectivity for Virtual Networks).
- VPN ExpressRoute inter-connectivity.
- Azure Route Table, Azure Firewall, and encryption for private connectivity.
SKUs
| Virtual WAN type | Hub type | Available configurations |
|---|---|---|
| Basic | Basic | Site-to-site VPN only |
| Standard | Standard | ExpressRoute User VPN (P2S) VPN (site-to-site) Inter-hub and VNet-to-VNet transiting through the virtual hub Azure Firewall NVA in a virtual WAN |
Virtual Hubs
The Virtual Hub is a Microsoft-managed virtual network. It is a minimum size address space of a /24. As the user, you do not have to provision subnets, as the VWAN creates the appropriate subnets in the virtual hub as it requires for VPN Gateways, Express Routes , VPNS, Firewalls etc. Routing within a virtual hub is managed by Border Gateway Protocol, but you can also apply your own Azure Route Table to a Virtual Hub.
A Virtual Hub is deployed to a region with its own name, its own Address Space, and a capacity measured in #Routing Infrastructure units.
Routing Infrastructure Units
The capacity scales linearly with RUI 3 supporting an aggregate throughput of 3 Gbps and 3000 VMs. The largest RUI is RUI 50 that supports a throughput of 50 Gbps and 50000 VMs. RUI 2 is the exception, supporting a throughput of 3 Gbps and 2000 VMs. Full table is available on the Microsoft Docs.
| Routing infrastructure unit | Aggregate throughput Gbps |
Number of VMs |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | 2000 |
| 3 | 3 | 3000 |
| 4 | 4 | 4000 |
| ... | ... | ... |
| 48 | 48 | 48000 |
| 49 | 49 | 49000 |
| 50 | 50 | 50000 |
Network Virtual Appliances
Virtual WAN has the ability to deploy managed NVA's such as such as Barracuda CloudGen WAN, Cisco Cloud OnRamp for Multi-Cloud, and VMware SD-WAN. The Managed NVA capability is unique to Azure Virtual WAN, and can not be deployed to a standalone Azure Virtual Network.
Although each NVA offers support for different CPEs and has a slightly different user experience, they all offer a Managed Application experience through Azure Marketplace, NVA Infrastructure Unit-based capacity and billing, and Health Metrics surfaced through Azure Monitor.
When deploying the NVA, an application placeholder is deployed to the Customers resource group, but majority of the resources are in a hidden Managed resource group. Further configuration for the NVA is completed as per the norms of the NVA appliance, through their portals and tools.
NVA Infrastructure Units
The capacity for the NVA is measured in Infrastructure Units, with each unit being 500 Mbps of aggregate bandwidth. Each NVA can have 1-80 Units.
Site to Site VPN
A Site to Site VPN can be configured using a Azure Virtual Network Gateway either on deployment of the Virtual Hub or post deploy. Routing is configured using BGP Routing with a default AS Number of 65515.
Gateway Scale Units
The S2S capability is measured in Gateway scale units. Each Gateway scale unit is a redundant pair of 500 Mbps capability, supporting 500 clients. This scales linearly, assumingly up to 50 units[1]
Point to Site VPN
A Point to Site VPN can be configured using a Azure Virtual Network Gateway either on deployment of the Virtual Hub or post deploy. A Point to Site VPN can use either OpenVPN Protocol, Secure Socket Tunnelling Protocol or IKEv2. Users can either be authenticated by Azure Certificates, Entra ID, or AD DS with RADIUS
Citation needed ↩︎