How to Extract or Unzip tar.gz Files from Linux Command Line

A tar.gz file contains several compressed files to save storage space, as well as bandwidth during the downloading process. The .tar file acts as a portable container for other files and is sometimes called a tarball. The .gz part of the extension, stands for gzip, a commonly-used compression utility.
In this guide you will learn how to extract or unzip files from tar.gz files using command-line in Linux.
 tutorial on extracting files using tar.gz from command line
tutorial on extracting files using tar.gz from command line
- Access to a command-line/terminal window
- The utility (included by default)
- The gzip utility (included by default)
Extracting tar.gz Files in Linux
Using gzip Utility
Gzip by default, extracts the file in the current directory. In this example the file is located in the Documents directory.
Below, we have used the file named test.txt. Use the name of the file you want to compress instead.
to compress a single file with gzip enter the command in your terminal window:
gzip test.txt
After zipping the file, enter the command ls to confirm that the file has been compressed. The output confirms that the file now has a .gz extension.
 confirming that the file has been compressed
confirming that the file has been compressed
To decompress a file, use the gunzip command:
gunzip test.txt
Again, use the ls command to confirm the extension of the file.

To compress all the .txt files in a particular directory, type in:
The * sign is a wildcard, which means “any number of any characters.” This command would work on any (and all) filenames with the extension .txt.
This technique can be used on other file types including gzip.txt, .jpg, and .doc.
When you run gzip on multiple files at once, the system generates a compressed copy of each file. This can clutter up a directory quickly! Fortunately, there’s another tool to manage multiple files at once.
Using tar Utility
A tar.gz file is a combination of a .tar file and a .gz file. It is an archive file with several other files inside it, which is then compressed.
You can unzip these files the same way you would unzip a regular zipped file:
tar –xvzf documents.tar.gz
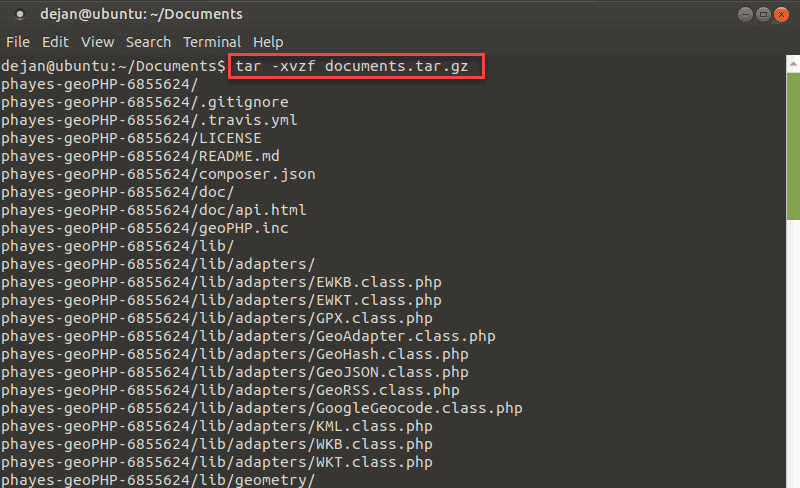 output in the linux terminal when extracting a tar.gz file
output in the linux terminal when extracting a tar.gz file
The basic command is , followed by four options:
- – instructs tar to extract the files from the zipped file
v– means verbose, or to list out the files it’s extractingz– instructs tar to decompress the files – without this, you’d have a folder full of compressed filesf– tells tar the filename you want it to work on
To list the contents of a .tar file before you extract it, enter:
tar –tzf documents.tar.gz
To instruct tar to put the extracted unzipped files into a specific directory, enter:
tar –xvzf documents.tar.gz –C /home/user/destination
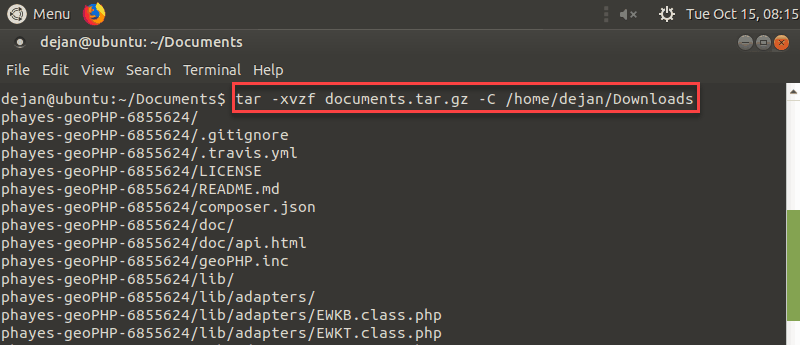 how to unzip a tar.gz file to a specific destination in Linux
how to unzip a tar.gz file to a specific destination in Linux
To create a file, use the following command:
Similar to the tar command, it condenses all the content located in the /home/user/Documents directory into a single file, called documents.tar.gz. The addition of the –z option is what signals tar to compress the files.
To add multiple files to a tar file, use the command:
This copies the contents of your Documents folder into a single file, called documents.tar. The options -cvf work as follows:
c– creates a new archivev– verbose, meaning it lists the files it includesf– specifies the name of the file
To extract the files from a .tar file, enter:
tar –xvf documents.tar
This command extracts and lists all files from the documents.tar file. The -x option tells tar to extract the files.

You can also use xargs with tar to create a tar.gz archive and populate it with files from the find command.
Note: Some graphical interfaces include a tool for managing tar.gz files without the command-line. Simply right-click the item you want to compress, mouseover compress, and choose tar.gz. You can also right-click a tar.gz file, mouseover extract, and select an option to unpack the archive.
This tutorial explains how to use the tar tool, the gzip tool, and how to utilize them together to work with tar.gz files. You are now ready to extract or unzip any tar.gz file.